
  | Claus, C., Slavin, M., Ansseau, E., Lancelot, C., Bah, K., Lassche, S., Fievet, M., Greco, A., Tomaiuolo, S., Tassin, A., Dudome, V., Kusters, B., Decleves, A.-E., Laoudj-Chenivesse, D., van Engelen, B. G. M., Nonclercq, D., Belayew, A., Kalisman, N., & Coppée, F. (07 March 2023). The double homeodomain protein DUX4c is associated with regenerating muscle fibers and RNA-binding proteins. Skeletal Muscle, 13 (1), 5. doi:10.1186/s13395-022-00310-y  Peer Reviewed verified by ORBi Peer Reviewed verified by ORBi |
Dudome, V., Genva, S., Coppée, F., & Decleves, A.-E. (31 January 2020). Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress response induced by palmitate in human muscle cells [Paper presentation]. 14 th meeting of the FRS-FNRS Contact Group on Oxidative Processes and Antioxidants, Mons, Belgium. |
Dudome, V., Coppée, F., & Declèves, A.-E. (31 January 2020). Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress response induced by palmitate in human muscle cells [Paper presentation]. 14th meeting of the FRS-FNRS Contact group on Oxidative Proceses and Antioxidants, UMONS, Belgium. |
  | Claus, C., Dudome, V., Derenne, A., Coppée, F., & Decleves, A.-E. (2019). Draw my phD. |
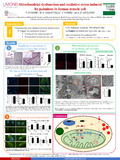  | Dudome, V., Coppée, F., Decleves, A.-E., & Dabauvalle, M. C. (29 April 2019). Lipotoxicity and oxidative stress induced by palmitate in human muscle cells [Poster presentation]. 26th European Congress on Obesity, Glasgow, Unknown/unspecified. |
Dudome, V. (2019). Quand la graisse s'installe dans les muscles. |
Claus, C., Dudome, V., Delcourt, M., & Juszczak, F. (2019). Who killed Pr. Watson? |
Dudome, V., Coppée, F., Decleves, A.-E., & Dabauvalle, M. C. (13 January 2019). Lipotoxicity and oxidative stress induced by palmitate in human muscle cells' [Poster presentation]. Ecole doctorale EDT-BCMB (Biologie Cellulaire et Moléculaire & Biochimie - FNRS), Bruxelles, ULB - Campus Erasme, Belgium. |
Dudome, V., Coppée, F., & Decleves, A.-E. (31 October 2018). Lipotoxicity and oxidative stress induced by palmitate in human muscle cells [Poster presentation]. 7th European worshop on lipid mediators, Bruxelles, Belgium. |
Dudome, V., Coppée, F., & Declèves, A.-E. (18 February 2018). Lipotoxicity and oxidative stress induced by palmitate in human muscle cells [Poster presentation]. Scientific Meeting FNRS Contact Group 'Oxidative Processes and Antioxidants', Namur, Belgium. |
  | Vanderplanck, C., Tassin, A., Ansseau, E., Lancelot, C., Derenne, A., Conotte, S., Dudome, V., Leroy, B., Wilton D., S., Laoudj-Chenivesse, D., Wattiez, R., Legrand, A., Belayew, A., & Coppée, F. (14 March 2016). 'Antisense strategies targeting DUX4 and DUX4c for the treatment of Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy.' [Poster presentation]. 5th International Congress of Myology, Lyon, France. |
Vanderplanck, C., Tassin, A., Ansseau, E., Lancelot, C., Derenne, A., Conotte, S., Dudome, V., Leroy, B., Wilton D., S., Laoudj-Chenivesse, D., Wattiez, R., Legrand, A., Belayew, A., & Coppée, F. (2015). Antisense strategies targeting DUX4 and DUX4c for the treatment of Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy [Paper presentation]. International World Muscle Society congress, Brighton, United Kingdom. |
Vanderplanck, C., Tassin, A., Ansseau, E., Lancelot, C., Derenne, A., Conotte, S., Dudome, V., Leroy, B., Wilton D., S., Laoudj-Chenivesse, D., Wattiez, R., Legrand, A., Belayew, A., & Coppée, F. (22 May 2015). Antisense strategies targeting DUX4 and DUX4c for the treatment of Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy [Poster presentation]. Journée UMHAP from lab to bedside, Mons, Belgium. |
Vanderplanck, C., Tassin, A., Ansseau, E., Lancelot, C., Derenne, A., Conotte, S., Dudome, V., Leroy, B., Wilton D., S., Laoudj-Chenivesse, D., Wattiez, R., Legrand, A., Belayew, A., & Coppée, F. (17 April 2015). Antisense strategies targeting DUX4 and DUX4c for the treatment of facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD [Poster presentation]. Novel Therapies for monogennic diseases, Paris, France. |
Vanderplanck, C., Tassin, A., Ansseau, E., Lancelot, C., Derenne, A., Conotte, S., Dudome, V., Leroy, B., Wilton D., S., Laoudj-Chenivesse, D., Wattiez, R., Legrand, A., Belayew, A., & Coppée, F. (15 April 2015). Antisense strategies targeting DUX4 and DUX4c for the treatment of Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy [Poster presentation]. symposium de thérapie génique du Collège de France, Paris, France. |